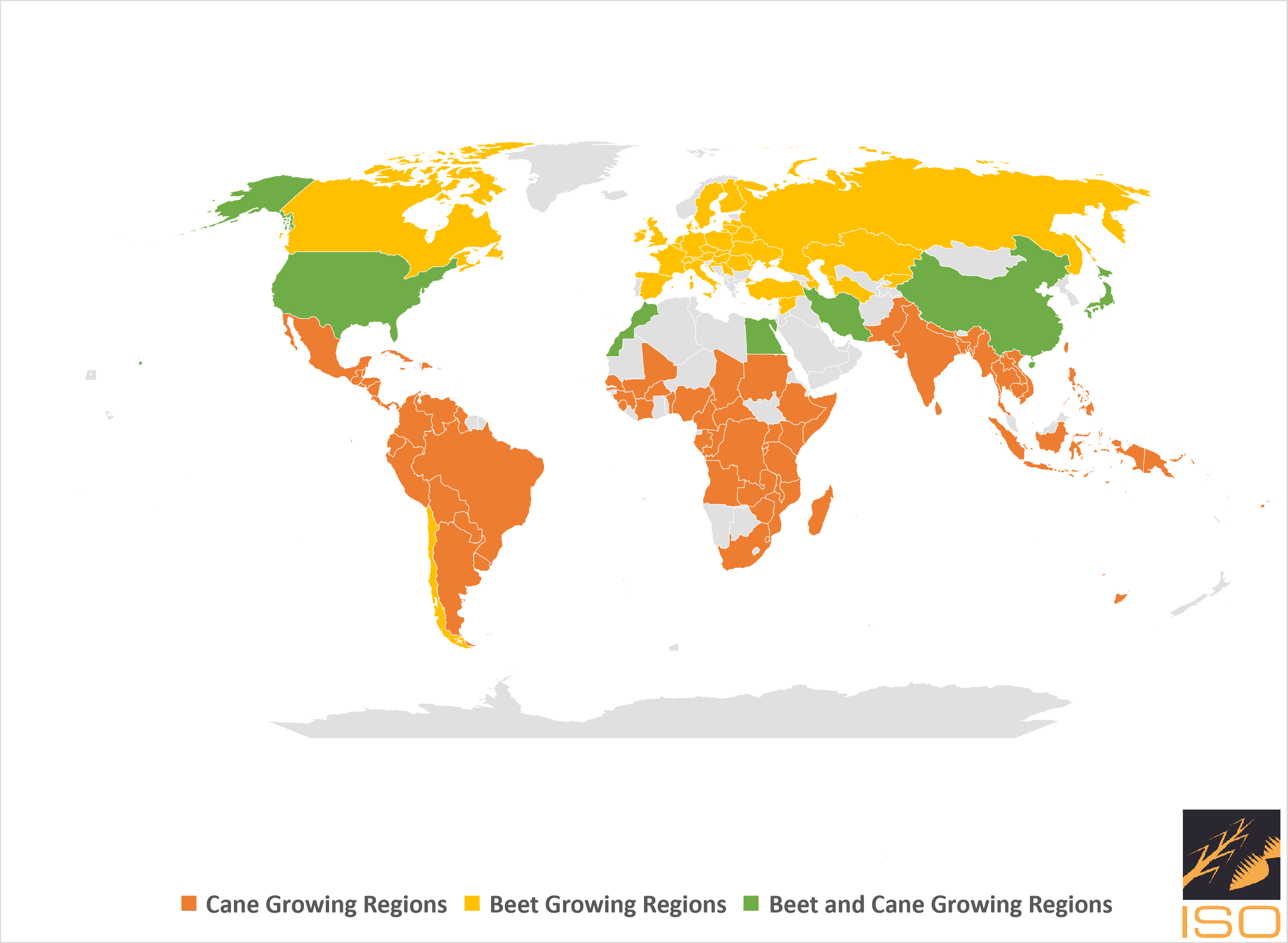
World Sugar cane and Sugar beet Growing Countries
Sugar Cane
Sugar cane (Saccharum officinarum) is a tall, perennial grass widely cultivated for its high sugar content. This plant plays a pivotal role in the global sugar industry as a primary source of sucrose. With its origins in Southeast Asia, sugar cane has been cultivated for thousands of years and has spread to various tropical and subtropical regions around the world.
The sugar content in sugar cane is concentrated in its stalks, which are harvested for processing. The extraction process involves crushing the cane to extract the juice, which is then subjected to various refining and crystallization steps to produce sugar in different forms.
Beyond its significance in sugar production, sugar cane is also a versatile crop. In addition to sugar, it is used to produce molasses, ethanol, and bioenergy. The fibrous residue known as bagasse, left after juice extraction, is utilized for energy production or as a raw material in various industries.
The cultivation of sugar cane has economic importance for many countries and communities, providing income and employment opportunities. However, it also raises environmental and social considerations, as large-scale cultivation can impact ecosystems and may involve labor-intensive harvesting practices.
Overall, sugar cane stands as a crucial global crop with a rich history, contributing significantly to the world's sugar supply and playing a multifaceted role in various industries and economies.
Sugar Beet
Sugar beet (Beta vulgaris) is a plant cultivated for its sugar-rich taproot, and it serves as a vital source for sugar production. Originating in Europe, sugar beet has become a significant crop globally, thriving in temperate climates. Unlike sugar cane, sugar beet is well-suited for cultivation in regions with cooler weather.
The primary focus of cultivating sugar beets lies in the extraction of sucrose from the beet's thick root. When mature, these roots are harvested and undergo a processing sequence involving slicing, diffusion, and crystallization to extract and refine the sugar. The resulting sugar can be utilized in various food and industrial applications.
Sugar beet cultivation has gained prominence as an alternative to sugar cane in regions where climatic conditions are less favorable for sugarcane growth. This crop has played a pivotal role in providing a locally viable source of sugar and reducing dependence on imported sugar in certain areas.
Apart from its significance in the sugar industry, sugar beet has also found application in animal feed and bioenergy production. The pulp and by-products generated during sugar extraction can be repurposed for these purposes, contributing to the overall sustainability of sugar beet cultivation.
In essence, sugar beet stands as a crucial crop in the global agricultural landscape, offering a reliable source of sucrose for various industries while presenting an adaptable alternative to sugar cane in certain climates.
Future Events
18th CITI-ISO-DATAGRO New York Sugar & Ethanol Conference 2025
14 May 2025 - 583 Park Avenue - New York - NY 10065 - USA
View Event Details
66th International Sugar Council - Costa Rica
26 May 2025 - Marriot Hotel Hacienda Belén, Costa Rica
View Event Details
ISO INTERNATIONAL SEMINAR
02 Dec 2025 -
View Event Details
Publications